Overcenter Valve vs Counterbalance Valve: Which is Right for Your Application?
2024-01-29In hydraulic systems, it is important to understand the difference between an overcenter valve and a counterbalance valve. Although the two are similar in some functions, for example, both can be used to prevent the load from free falling, there are some differences in their working principles and application scenarios.
The difference between over-center valve and balanced valve
The overcenter valve (also called return check valve) is a pilot-assisted relief valve with a free-flow check function. The so-called pilot ratio refers to the ratio between the pilot pressure area and the overflow area. This ratio is critical to the pressure range over which the valve can go from closed to fully open, especially under varying load pressures. A low pilot ratio means a larger pilot pressure difference is required to fully open the valve. As the load pressure increases, the required difference in pilot pressure for various pilot ratios becomes smaller.
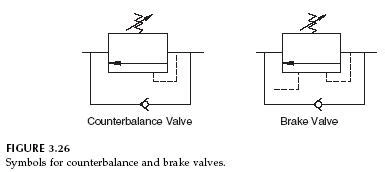
The counterbalance valve is a valve used to prevent the load cylinder from falling, providing smoother operation. Compared to pilot-operated check valves, counterbalance valves do not cause jerky movements when the controlled load decreases. Counterbalance valves typically employ cone or spool pressure control elements, with cone counterbalance valves used to prevent cylinder drift and spool counterbalance valves used as brake valves in hydraulic motor applications.
Application selection
The use of counterbalance valves in moving cylinders is necessary when loads may cause the actuator to overspeed faster than the pump. Alternatively, balancing valves can also be used in pairs of cylinders: pilot pressure will open the valve of the heaviest loaded cylinder first, which will cause the load to be transferred to the other cylinder, with the associated valve still closed at this time, requiring the opening of The pilot pressure is less.
When choosing between an overcenter valve or a balanced valve, the stability of the machine needs to be considered. More unstable loads should use a lower pilot ratio to optimize machine stability. The type of valve in the design also affects the inherent stability of the product. For example, the over-center valve solution designed by Eaton uses a direct-acting design to make the main spring have a higher stiffness. Therefore, when the load pressure changes, the valve will not react so quickly, reducing flow changes and providing an overall System stability.