Introduction to Solenoid Valve: A Critical Component in Automation Systems
2024-02-18Introduction to solenoid valve
The solenoid valve is a basic component of automation controlled by electromagnetism. This valve belongs to the category of actuators, which adjust the direction, flow rate, speed and other parameters of the medium (fluid or gas) in industrial control systems. Solenoid valves can be matched with different circuits to achieve precise and flexible control. They are found in a variety of applications, such as shutting off, releasing, dosing, dispensing or mixing fluids in liquid and gas control systems.
How the solenoid valve works
The core of a solenoid valve is composed of an electromagnet (coil) and a valve. When the electromagnet is energized, it generates magnetic force that attracts the valve core to complete the opening or closing action, thereby controlling the flow of fluid. Solenoid valves usually have direct-acting, pilot-operated and other designs to adapt to different working conditions. When the direct-acting solenoid valve is energized, the electromagnetic force lifts the closing member, and when the power is turned off, the spring force or medium pressure closes it; while the pilot-operated solenoid valve uses the electromagnetic force generated by energization to open the pilot hole, causing the upper chamber pressure to rapidly decrease, forming a pressure The difference drives the main valve to open
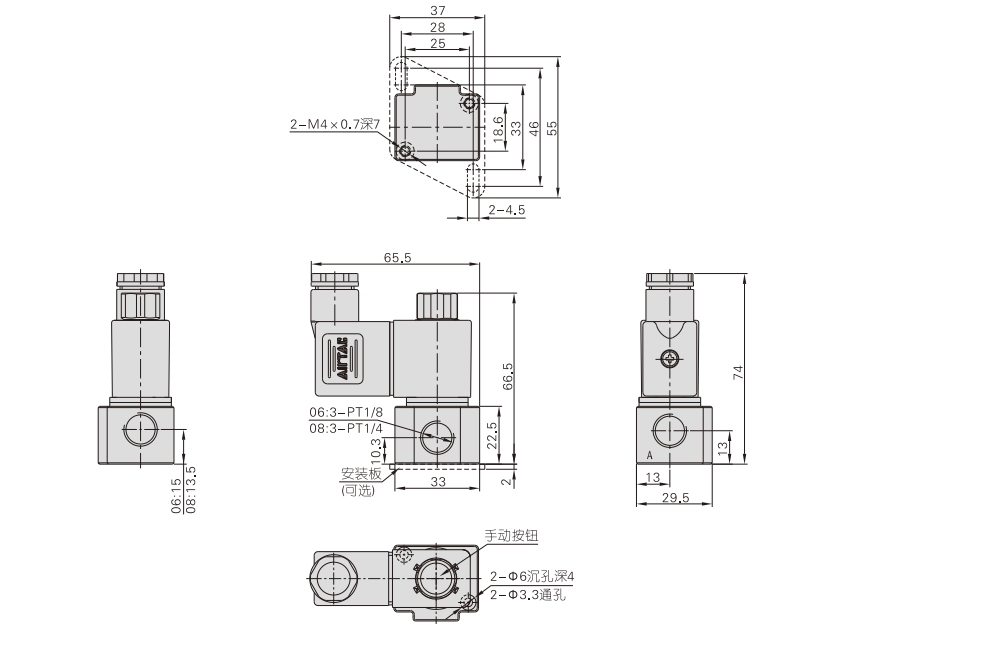
Types and selection of solenoid valves
According to different working principles, solenoid valves can be divided into direct-acting, distributed direct-acting and pilot-operated. In addition, according to the differences in valve structure and materials, it can be further divided into multiple subcategories, such as direct-acting membrane structure, pilot membrane structure, direct-acting piston structure, etc. When selecting a solenoid valve, you should follow the four principles of safety, applicability, reliability and economy, and consider factors such as working conditions, pipeline parameters, fluid parameters, and pressure parameters.
The material composition of the solenoid valve must also be considered when selecting it. In particular, the valve body and sealing parts need to select corresponding materials according to the type of medium controlled (such as water, gas, oil, etc.) and the environment (such as temperature, corrosiveness, etc.) to ensure Compatibility and durability.
Common uses and functions
Solenoid valves are widely used in various automation systems, such as water treatment, pneumatic or hydraulic control, medical equipment, food processing, etc. They can achieve fast and safe switching, provide high reliability, long service life and compact design, and can accurately control the flow of media, thus playing a vital role in automatic control systems.
Overall, understanding the basic functions and selection knowledge of solenoid valves is critical to their correct use in automated systems. Following the correct selection principles and combining with actual application requirements can ensure the effective operation of the solenoid valve in the control system.