Exercise 4-1: Indirect Control Using Pilot-Operated Valves
2024-07-29Understanding Pilot-Operated Valves
Pilot-operated valves (POVs) are a type of control valve that utilize a small, auxiliary valve (the pilot) to regulate the flow of fluid through a larger main valve. The pilot valve, operated by a pressure signal or other input, controls the position of the main valve's spool or piston. This indirect control method offers several advantages, including precise control, increased sensitivity, and the ability to handle high flow rates.
How Pilot-Operated Valves Work
1.Pilot Valve Activation: A pressure signal, electrical signal, or mechanical input activates the pilot valve.
2.Pilot Valve Controls Main Valve: The pilot valve's movement modulates the flow of fluid to a diaphragm or piston in the main valve.
3.Main Valve Position: The pressure differential created by the pilot valve causes the main valve to open or close, controlling the flow of the main fluid stream.
Advantages of Pilot-Operated Valves
• Precise Control: Pilot-operated valves offer fine-tuned control over fluid flow, making them ideal for applications requiring precise regulation.
• High Flow Rates: These valves can handle high flow rates while maintaining precise control.
• Remote Operation: Pilot-operated valves can be controlled remotely using various input signals, enabling automation and integration into larger control systems.
• Increased Sensitivity: Pilot-operated valves are highly sensitive to changes in input signals, allowing for rapid response times.
• Safety Features: Many pilot-operated valves incorporate safety features such as fail-safe mechanisms to prevent hazardous conditions.
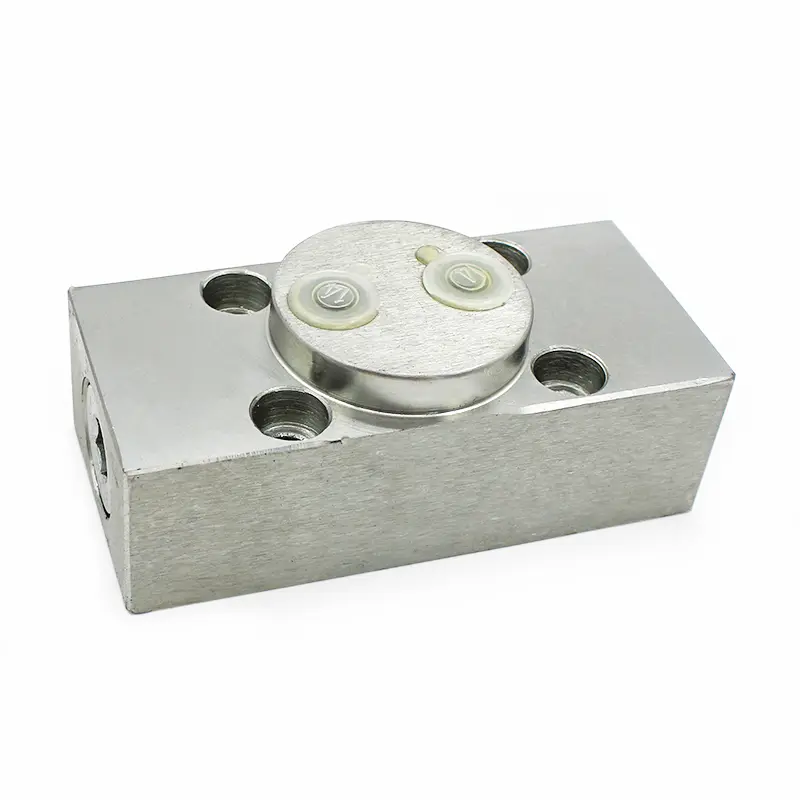

Applications of Pilot-Operated Valves
Pilot-operated valves find extensive use in various industries, including:
• Hydraulic Systems:
° Controlling hydraulic cylinders for precise positioning
° Regulating pressure in hydraulic circuits
° Implementing complex sequencing operations
• Pneumatic Systems:
° Controlling pneumatic actuators for automation tasks
° Regulating air pressure in pneumatic circuits
• Process Control:
° Controlling flow rates in chemical processes
° Regulating pressure in pipelines
° Maintaining temperature in industrial processes
Exercise Tasks and Considerations
To effectively complete Exercise 4-1, consider the following tasks and factors:
• Identify the Components: Familiarize yourself with the various components of a pilot-operated valve, including the pilot valve, main valve, and connecting passages.
• Understand the Operating Principle: Grasp the underlying principles of how pressure differentials and fluid flow interact to control the main valve.
• Analyze Different Types: Explore various types of pilot-operated valves, such as pressure-compensated, flow-controlled, and electrically actuated valves.
• Consider Applications: Think about specific applications where pilot-operated valves would be beneficial and how they can improve system performance.
Design a Control Circuit: Design a simple hydraulic or pneumatic circuit incorporating a pilot-operated valve to control a specific process or function.
Potential Exercise Questions
• How does a pilot-operated valve differ from a direct-acting valve?
• What are the advantages of using a pilot-operated valve in a hydraulic system?
• Design a pilot-operated valve circuit to control the speed of a hydraulic cylinder.
• Explain how a pilot-operated relief valve works and its role in safety systems.
• Discuss the factors that influence the selection of a pilot-operated valve for a particular application.
By completing Exercise 4-1, you will gain a solid understanding of the principles, applications, and advantages of pilot-operated valves. This knowledge will empower you to design and implement effective control systems in various industrial settings.
Note: To provide a more tailored response, please provide additional details about the specific requirements of your exercise, such as:
• The type of fluid being controlled (hydraulic oil, air, etc.)
• The desired level of control (on/off, proportional, etc.)
• Any specific constraints or limitations
With this information, I can provide more targeted guidance and examples.